Discover the Blyscan™ Glycosaminoglycan Kit: Your go-to Solution for reliable sGAG and Proteoglycan Analysis! Our versatile, widely cited kit utilizes a dye-binding approach to quantitatively measure sulfated glycosaminoglycans (sGAG) and proteoglycans in cells, tissues, and fluids from in-vivo and in-vitro sources.
Description
The Biocolor Blyscan™ Glycosaminoglycan (sGAG) Assay enables quantitative measurement and analysis of sulfated proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans (sGAG).
Soluble sGAGs may be assayed directly, whereas solid materials will require a preliminary papain extraction.
The assay can be used to measure the total sGAG content and can also be adopted to determine the O- and N-sulfated glycosaminoglycan ratio within test samples.
Suitable Samples
In-vivo:
- Solid samples, including cartilage, bone, connective tissue, tumor tissue
-
Liquid samples, including fluids such as urine, amniotic fluid, or synovial fluid
In-vitro:
- Solid samples, such as deposited ECM on 2D/3D culture surfaces by enzymatic treatment
- Liquid samples, Culture media during 2D/3D cell culture
The assay requires that sulfated polysaccharides or sGAGs are in a soluble form. A preliminary enzymatic extraction step is required for solid samples (enzyme not supplied with kit).
The assay is not suitable for use with samples containing alginates or that comprise degraded sulfated disaccharide fragments.
Principle of Method
Colorimetric Assay, Dimethylmethylene Blue Assay (DMMB)
The dye label used in the assay is 1,9-dimethylmethylene blue (DMMB) and the dye is employed under conditions that provide a specific label for the sulfated polysaccharide component of proteoglycans or the protein free sulfated glycosaminoglycan chains.
Step 1. Blyscan dye reagent contains DMMB dye in an optimized buffer. Addition of Dye reagent to samples containing sGAG results in the formation of a dye/sGAG complex due to a charge interaction between dye and GAG sulfate groups.
Step 2. Over a 30 minute incubation Dye-labelled sGAGs precipitate out of solution and are collected by centrifugation. Following removal of unbound dye, the remaining bound dye is released from the complex by addition of dye dissociation reagent. Released dye is quantified spectrophotometrically.
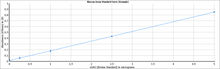
Step 3. The sGAG content of unknown samples may be quantified by comparison against a calibration curve prepared using a standard of purified Chondroitin-4-sulfate supplied with the kit.
The Blyscan Dye reagent is formulated to minimize binding to other charged sample components such as nucleic acids, a problem with some older dye-based sGAG assays.

Test Sample Composition
An extensive range of mammalian proteoglycans have been measured using this assay. The following sGAG, either still attached to the peptide/protein core, or as free chains can be assayed:
- chondroitin sulfates (4- & 6-sulfated)
- keratan sulfates (alkali sensitive & resistant forms)
- dermatan sulfate
- heparan sulfates (including heparins)
Hyaluronate is not detected by the Blyscan Assay. The presence of hyaluronate in test samples does not interfere with the measurement of sGAG.
Specifications
| Product Category: | |
|
Detection Method: |
Colorimetric Detection (656 nm) |
| Assay Range:https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0563/4487/1064/files/Blyscan-manual-webopt.pdf?v=1672706553 | 0 - 50 µg/ml |
| Limit of Detection: | 2.5 µg/ml |
| Sensitivity: | 0.5 µg |
| Assay Run-Time: |
1 hour |
| Measurements Per Kit: | 110 in total (allows a maximum of 48 samples to be run in duplicate alongside a standard curve) |
| Storage (unopened kit): | Room Temperature (RT) |
| Manufacturer: | Biocolor Ltd. |
| Country of Origin: | United Kingdom |
Kit Contents
The standard size Blyscan™ Glycosaminoglycan kit (cat. no. B1000) contains:
- Blyscan Dye Reagent (1x 110 ml)
- sGAG Reference Standard (1x 5 ml, 100 µg/ml Bovine tracheal chondroitin 4-sulfate)
- Dissociation Reagent (1x 110 ml)
- Sodium Nitrite (1x 15 ml)
- Acetic Acid (1x 15 ml)
- Ammonium Sulfamate (1x 15 ml)
- 1.5 ml micro-centrifuge tubes for dye-labelling reaction
- Assay kit manual
NOTE: Additional reagents may be required for sample preparation prior to assay. Consult manual or contact us for further details.
Applications
- fibrous and hyaline cartilages
- arteries, heart, lung, skin and other material containing extracellular matrix (connective tissue), and solid tumors
- extracellular matrix components that may be released by live cells into culture medium
- soluble sGAG from synovial fluid, urine and gel chromatography fraction aliquots
Technical Video
Other Names/Synonyms
Blyscan sGAG Assay, s-glycosaminoglycan, sulfated glycosaminoglycan
Resources
2025 Product References
- Zhou, Jialiang et al. “Decellularized Adipose Matrix Rejuvenates Photoaged Skin through Immune Microenvironment Modulation.” BME frontiers vol. 6 0166. 4 Aug. 2025, doi:10.34133/bmef.0166
- Hussein, Kamal H et al. “Efficacy of xenogeneic fresh and lyophilized amniotic membranes on the healing of experimentally induced full-thickness skin wounds in dogs.” Scientific reports vol. 15,1 15605. 4 May. 2025, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-95023-9
- Bhattacharyya, Sumit, and Joanne K Tobacman. “Interactions of CFTR and Arylsulfatase B (ARSB; N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase) in Prostate Carcinoma.” International journal of molecular sciences vol. 26,9 4350. 3 May. 2025, doi:10.3390/ijms26094350
- Breland, Austen N et al. “In Silico Insights into the Inhibition of ADAMTS-5 by Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis.” International journal of molecular sciences vol. 26,9 4093. 25 Apr. 2025, doi:10.3390/ijms26094093
- Shinoda, Chika et al. “N-glycan-modified α-L-iduronidase produced by transgenic silkworms ameliorates clinical signs in a Japanese macaque with mucopolysaccharidosis I.” Communications medicine vol. 5,1 128. 18 Apr. 2025, doi:10.1038/s43856-025-00841-7
- Singh, Pragya et al. “Comparative Study of Placental Allografts with Distinct Layer Composition.” International journal of molecular sciences vol. 26,7 3406. 5 Apr. 2025, doi:10.3390/ijms26073406
- Yang, Daniel et al. “Exosome-Seeded Cryogel Scaffolds for Extracellular Matrix Regeneration in the Repair of Articular Cartilage Defects: An In Vitro and In Vivo Rabbit Model Study.” Polymers vol. 17,7 975. 3 Apr. 2025, doi:10.3390/polym17070975
- Prithiviraj, Sujeethkumar et al. “Compositional editing of extracellular matrices by CRISPR/Cas9 engineering of human mesenchymal stem cell lines.” eLife vol. 13 RP96941. 28 Mar. 2025, doi:10.7554/eLife.96941
- Martino, Cameron et al. “SARS-CoV-2 infectivity can be modulated through bacterial grooming of the glycocalyx.” mBio vol. 16,4 (2025): e0401524. doi:10.1128/mbio.04015-24
- Galvez, Paul et al. “In vitro and in vivo assessment of a new acellular human amnion/chorion membrane device for guided bone regeneration.” Scientific reports vol. 15,1 5483. 14 Feb. 2025, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-88814-7
- Lee, Hyesook et al. “Oral trehalose improves histological and behavior symptoms of mucopolysaccharidosis type II in iduronate 2-sulfatase deficient mice.” Scientific reports vol. 15,1 4882. 10 Feb. 2025, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-88362-0
- Kopinski-Grünwald, Oliver et al. “Surface functionalization of microscaffolds produced by high-resolution 3D printing: A new layer of freedom.” Materials today. Bio vol. 31 101452. 3 Jan. 2025, doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101452
- Hurt, Sarah C et al. “Antibodies to recombinant human alpha-L-iduronidase prevent disease correction in cortical bone in MPS I mice.” Molecular therapy. Methods & clinical development vol. 33,1 101405. 2 Jan. 2025, doi:10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101405
Usage
This product is intended for laboratory research use only and is not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Background
Understanding Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and Proteoglycans:
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are members of the polysaccharide family that play a crucial role in various biological processes. They consist of repeated disaccharide units, typically of hexosamine, (N-acetylated or N-sulfated), paired with uronic acid (GlcA or IdoA) or galactose. Many GAGs have an overall "negative charge" due to the addition of sulfate groups. This charge influences cell and extracellular matrix interactions.
Common examples of GAGs include Chondroitin Sulfate, Dermatan Sulfate, Heparin, Heparan Sulfate, and Keratan Sulfate.
NOTE: Since Hyaluronic Acid is a non-sulfated GAG it cannot be detected by the Blyscan assay. If you need to measure hyaluronic acid, we recommend using the Biocolor Purple-Jelley™ Hyaluronic Acid Assay.
The Role of Glycosaminoglycans in Tissues:
GAGs and proteoglycans have essential functions in tissues and organisms including acting as a scaffold to provide biophysical support, and maintaining cartilage hydration. They also play a vital role in biochemical processes such as cell adhesion and signaling.
Ilex Life Sciences LLC is an official distributor of Biocolor Ltd.